Blog
Die Bewegung, die das Leben verändert
10-08-2023
Side effects NESA XSIGNAL® Is non-invasive neuromodulation safe?
What is non-invasive neuromodulation and how does it work?
Non-invasive neuromodulation is a therapeutic technique that regulates brain activity using external technologies, without requiring surgery or invasive procedures. It is based on the application of electrical, magnetic or focused ultrasound stimuli to modulate neuronal excitability and improve brain function.
For example, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic fields to generate weak electrical currents in specific areas of the brain. This non-invasive stimulation can influence neural circuits and provide therapeutic effects in conditions such as depression, chronic pain and neurological disorders.
Safety of non-invasive neuromodulation: Assessing risks and benefits
A major concern for patients and healthcare professionals is the safety of non-invasive neuromodulation. Fortunately, numerous studies and clinical trials have shown that this therapeutic modality is generally safe and well tolerated.
Compared to invasive neuromodulation, which involves the implantation of electrodes in the brain, non-invasive neuromodulation does not carry the risks associated with surgery, such as infection, bleeding or postoperative complications. In addition, because it does not require the insertion of devices into the body, risks related to allergic reactions or rejection of foreign materials are also reduced.
Safety and Side Effects of tDCS
In general, tDCS (transcranial direct current stimulation) is considered safe, with few side effects and complications. The most common side effects include irritation at the stimulation site, mild tingling sensations on the scalp and, in rare cases, temporary headaches or dizziness. However, these effects are generally mild and transient.
Safety and Side Effects of TMS
As for TMS (transcranial magnetic stimulation), it is also generally considered safe. The most common side effects include scalp discomfort during or after stimulation, as well as headaches. It is important to note that TMS is contraindicated in people with certain metal implants in or near the head, as the magnetic fields may interact with these implants.
Does NESA XSIGNAL® have any side effects?
Although non-invasive neuromodulation is generally considered safe, it is essential that treatments are performed by medical professionals trained and experienced in this technique. The dosage and location of stimulation must be precise to avoid unwanted effects.
In terms of NESA XSIGNAL® side effects, the most common side effects are mild and temporary, such as headaches, mild skin sensations or dizziness. These effects usually disappear shortly after treatment and rarely cause significant problems.
It is important to note that non-invasive neuromodulation is not suitable for all conditions and that each patient should be assessed individually to determine the suitability of treatment.
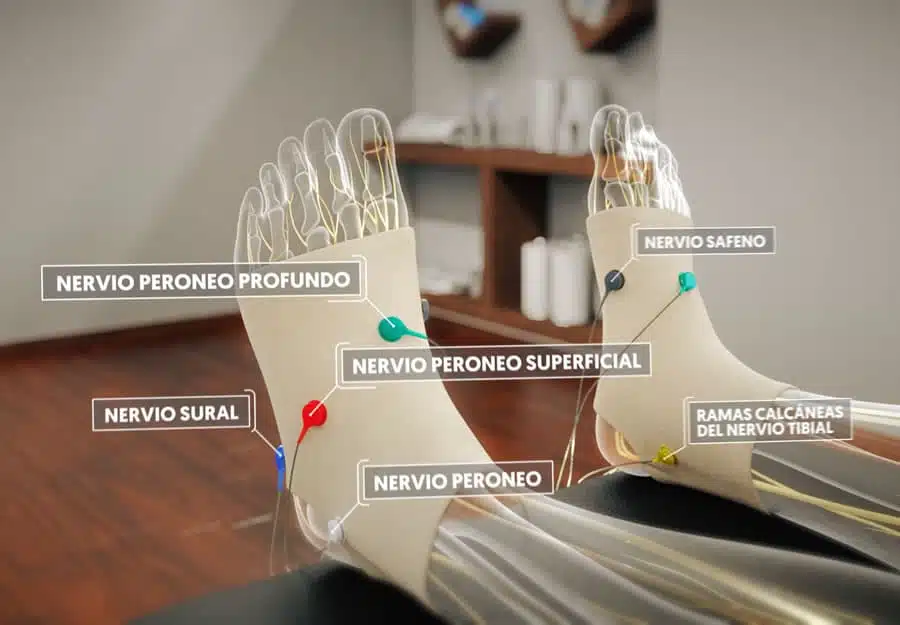
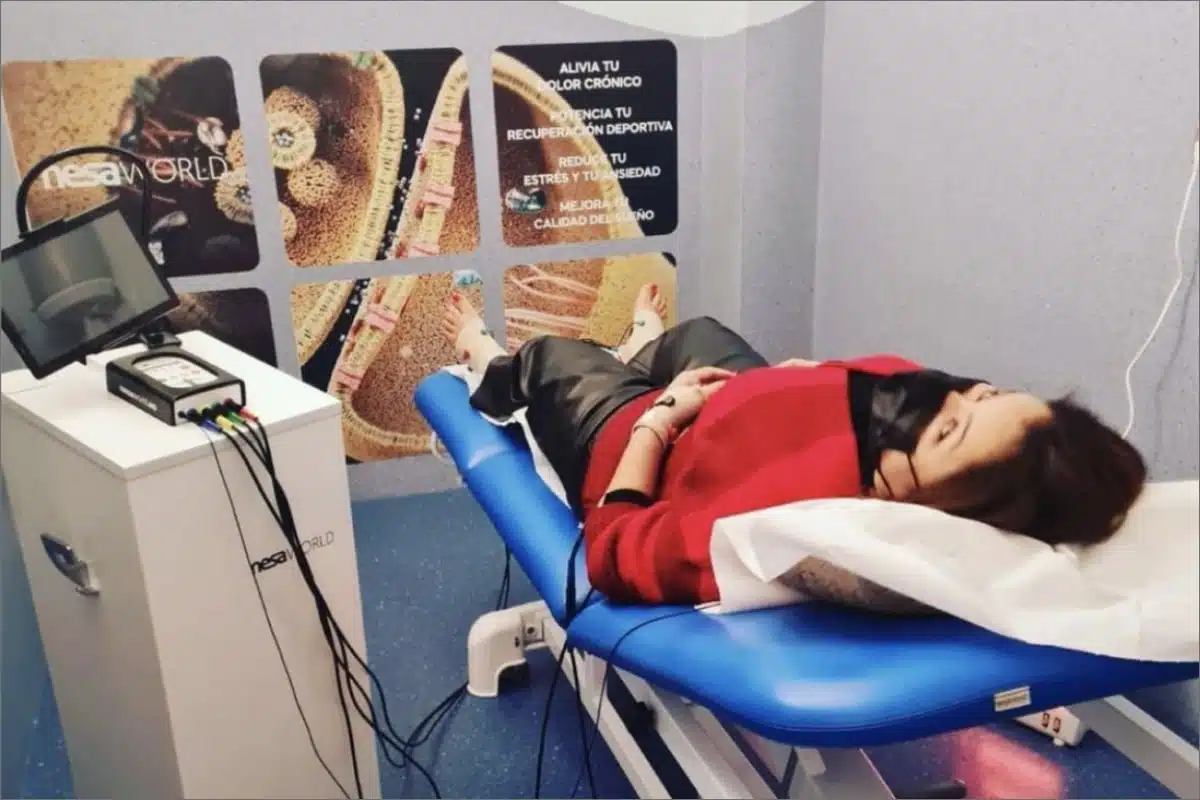
NESA XSIGNAL® is a medical device that delivers coordinated bioelectrical impulses to generate endogenous neuromodulatory responses in the body. These responses improve the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, restoring the electrical potential of all cell membranes in our body.
As for the side effects of NESA XSIGNAL®, no significant long-term effects have been found. What we must point out are certain contraindications that should be taken into account if you are using the treatment:
- Pacemakers or other electronic implants
- Pregnancy
- Open wounds or recent burns
- Thrombophlebitis
- Do not apply electrodes to damaged or ulcerated skin.
- Electrical phobia or hysteria
- Acute febrile processes
- Internal bleeding
Here are several studies on the safety and effectiveness of non-invasive neuromodulation in the treatment of different pathologies:
Efficacy and safety of the NESA XSIGNAL® device for the treatment of overactive bladder in urology.
Conclusions: A safe and promising approach
In conclusion, the side effects of NESA XSIGNAL® are negligible in terms of the benefit this device brings to the patient's health improvement. Non-invasive neuromodulation is a safe and promising approach for the treatment of various brain and neurological conditions. Its ability to improve brain function without invasive surgery and with minimal risk makes it a valuable therapeutic option for many patients. While treatments must be performed by trained professionals, the potential benefits of non-invasive neuromodulation in improving the quality of life of patients with neurological disorders are exciting and deserve further exploration and research.
In the future, it is expected that non-invasive neuromodulation will continue to expand its therapeutic horizons and provide new alternatives to improve the quality of life of patients facing neurological and psychiatric disorders. With proper adherence to ethical guidelines and regulation, we can expect non-invasive neuromodulation to become an integral component of modern medicine and a valuable tool in the treatment of various diseases.