Blog
Die Bewegung, die das Leben verändert
21-07-2023
How to improve the autonomic nervous system?
The nervous system is one of the most complex and fascinating systems in the human body. It is composed of various structures and sub-systems that work together to control and coordinate the body's functions. In this context, the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system play fundamental roles in regulating our physical and mental activities.
Structure of the Nervous System
- The central nervous system (CNS) is the processing and control centre of the body. It is made up of the brain and spinal cord, and is responsible for receiving, interpreting and sending nerve signals throughout the body.
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) extends from the central nervous system to the periphery of the body, encompassing the upper and lower limbs. Its main function is to transmit sensory information from organs and tissues to the central nervous system, as well as to send motor signals that enable the execution of voluntary movements and actions.
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is an essential part of the nervous system that regulates and controls the involuntary and automatic functions of the body. This system is divided into three main branches: the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
- The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for activating and mobilising the body in stressful or emergency situations. It is responsible for the ‘fight or flight’ response, increasing the heart rate, dilating blood vessels and releasing adrenaline, among other actions. In turn, it inhibits digestive functions to redirect the body's resources to the most critical areas in times of danger.
- On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for promoting relaxation and restoring the body's balance. It acts in situations of calm and rest, slowing the heart rate, stimulating digestion and promoting the elimination of waste from the body. This system allows all organic and vital functions to function properly during periods of relaxation and recovery.
- Finally, the enteric nervous system is responsible for regulating the functions of the digestive system, from the viscera to the brain. This system has an extensive network of neurons and nerve tissue distributed throughout the gastrointestinal tract, allowing it to control intestinal motility, nutrient absorption and other functions related to digestion.
Together, these nervous systems play a crucial role in regulating and coordinating our physical and mental activities. Understanding how they work provides us with tools to optimise our performance and improve our overall fitness. Throughout this text, we will explore how to improve performance and fitness through understanding and harnessing these nervous systems.
How to improve the functioning of the autonomic nervous system?
To find out how to improve the autonomic nervous system, there are different treatment options, such as medication, physical therapy, meditation and electrical stimulation. However, some of these treatments may have undesirable side effects or be invasive.
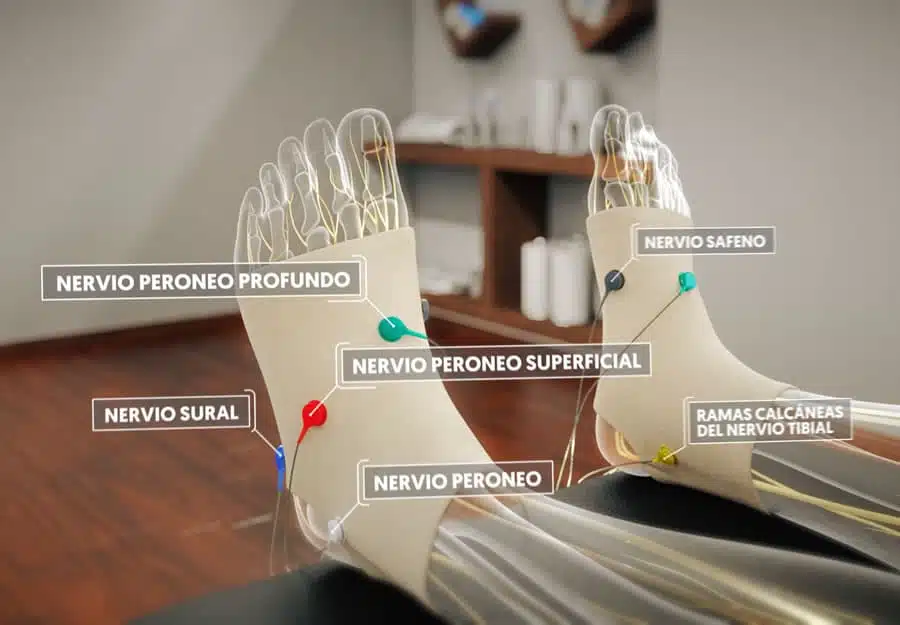
One innovative alternative is the non-invasive neuromodulation NESA XSIGNAL® , a technology developed by Japanese scientists that involves applying electrical microcurrents to the body using gloves and anklets with electrodes. These microcurrents act on the sensory pathways of the peripheral nervous system and optimise the body's bioelectrical balance.
NESA XSIGNAL® knows how to improve the autonomic nervous system by emitting electrical microcurrents that act on the sensory pathways of the peripheral nervous system and optimise the body's bioelectrical balance. These microcurrents are applied by means of gloves and anklets with electrodes that are coordinated with a directional electrode that is placed on the area to be treated.
The aim is to globally neuromodulate the organism, that is, to change the stimuli that the body itself is capable of creating. In this way, it is possible to regulate the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and improve its involuntary functions, such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestion and breathing.
NESA XSIGNAL® microcurrents are based on the principle of hormesis, i.e. the application of a low-intensity stimulus that elicits an adaptive response from the body. These microcurrents have a physiological frequency below 14-28 Hz, which is the range in which nerve cells communicate.
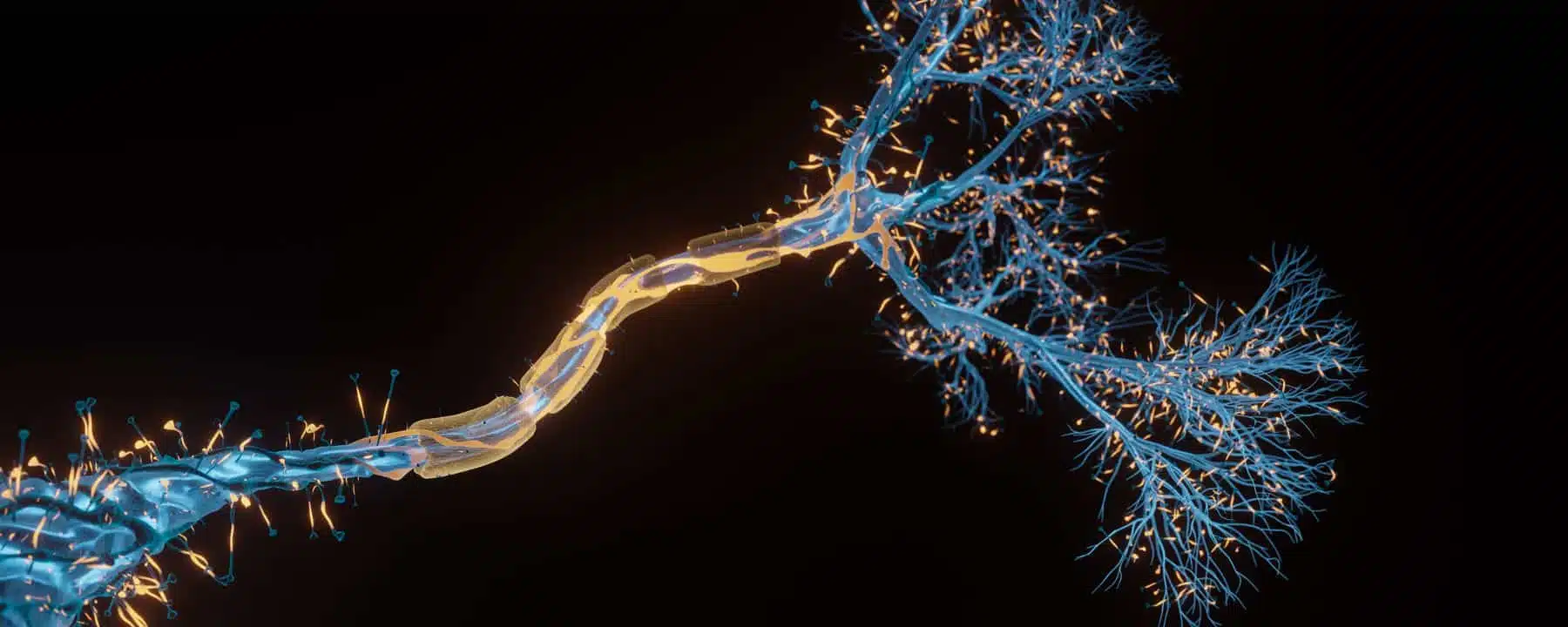
By applying these microcurrents to the sensitive pathways of the peripheral nervous system, the activity of neurons and glia, which are the cells responsible for the transmission and processing of information in the nervous system, is modulated. In this way, the tone of the autonomic nervous system is regulated and its response to different stimuli, such as pain, stress, inflammation or infection, is improved.
If you would like a professional to advise you on how NESA® can help you find out how to improve the autonomic nervous system, please contact us and we will get back to you as soon as possible.