Blog
The movement that changes lives

06-08-2024
Dysautonomia: How to understand and care for the autonomic nervous system
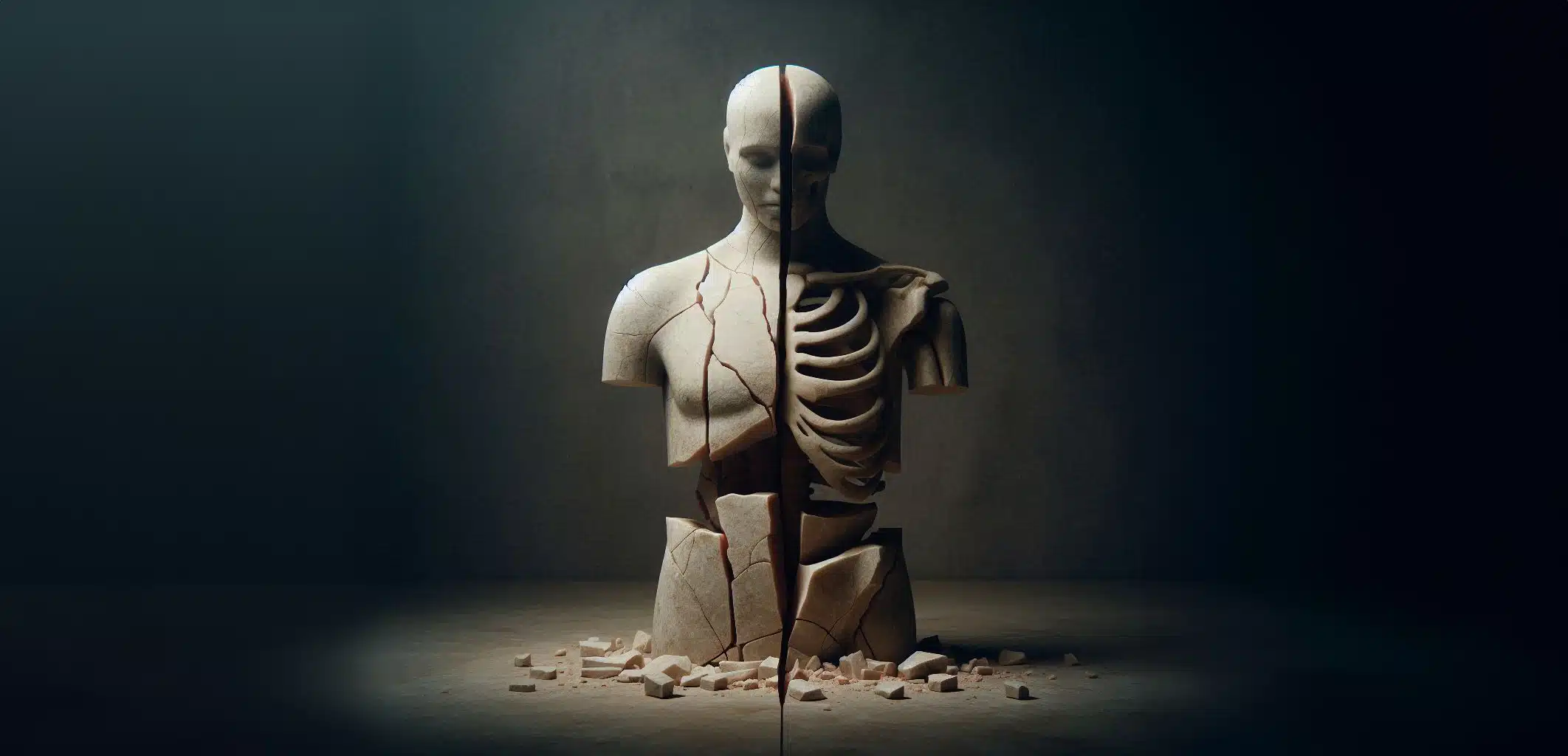
Dysautonomia and its relation to the autonomic nervous system
Our intention is for you to understand the meaning of the word dysautonomia and become familiar with it, but first we need to start by talking about the autonomic nervous system, also known as the involuntary nervous system. The ANS plays a fundamental role in the daily functioning of the human body, unconsciously regulating vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, metabolism, water and electrolyte balance, digestion, urination and defecation, pupil dilation and sexual response, among others. However, when this system becomes imbalanced, a condition known as dysautonomia can arise, significantly affecting the affected person's quality of life. In this article, we will explore the functions of the ANS, explain what dysautonomia is, address its symptoms and causes, as well as the role of NESA® Non-Invasive Neuromodulation technology in the recovery of patients with dysautonomia. Finally, we will offer a series of practical tips to keep the autonomic nervous system in balance.
Functions of the autonomic nervous system
Throughout the life of our blog, NESA life, we have repeated it many times: taking care of the autonomic nervous system is essential to keep our health in top shape. The ANS is divided into two main components: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system. The former is activated in ‘fight or flight’ situations, preparing the body for rapid action, increasing the heart rate, raising blood pressure and releasing stored energy. The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, promotes a state of ‘rest and digestion’, helping the body to calm down after danger and facilitating processes such as digestion and sleep regulation.
What is dysautonomia?
Dysautonomia is an umbrella term for a number of medical conditions that involve a malfunction of the ANS. This disorder affects the body's ability to perform essential automatic functions, which can lead to multiple and varied symptoms. While some forms of dysautonomia are temporary and manageable, others can be chronic and significantly debilitating
What causes dysautonomia
There are many types of autonomic nervous system disorders. They may be inherited or caused by injury, or by conditions such as diabetes, Parkinson's disease, an autoimmune disease or alcoholism. Sometimes the cause is unknown. This type of disorder that affects the balance of the autonomic nervous system is called dysautonomia.
Symptoms of dysautonomia
Symptoms of dysautonomia vary widely depending on the severity and type of disorder, but may include:
Heart rate and blood pressure variability
Heart rate and blood pressure are regulated by the autonomic nervous system. In people with dysautonomia, these can fluctuate significantly due to lack of proper regulation. This can manifest itself as palpitations or sensations of an irregular and fast or, conversely, very slow heartbeat. Fluctuations in blood pressure can lead to episodes of hypertension or hypotension, which are not only disconcerting, but can also be dangerous, affecting the perfusion of vital organs and general health.
Gastrointestinal problems such as IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
Dysautonomia can affect gastrointestinal motility, i.e. the ability of the digestive tract to move contents efficiently. This can lead to typical symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, such as abdominal pain, bloating, episodes of diarrhoea and constipation, and a general feeling of abdominal discomfort. These symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency, significantly complicating the affected person's daily life and nutrition.
Chronic and debilitating fatigue
One of the most common and challenging complaints for patients with dysautonomia is chronic fatigue. This type of fatigue goes beyond regular tiredness; it is a deep and persistent fatigue that does not improve with rest and can severely limit a person's ability to carry out their daily routine well. This fatigue is due to the body's constant overexertion in trying to maintain a state of homeostatic balance that the ANS cannot adequately regulate.
Dizziness and fainting, especially when standing up (orthostatic hypotension)
Orthostatic hypotension is a sudden drop in blood pressure when changing position (e.g. standing up from a sitting or lying position). This can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting. These symptoms occur because the ANS fails to quickly adjust blood pressure to changes in gravity and position, which is crucial for maintaining adequate cerebral blood flow.
Difficulties with body temperature regulation
The autonomic nervous system also influences the regulation of body temperature. In patients with dysautonomia, temperature control may be erratic, resulting in episodes of excessive sweating or, conversely, inability to sweat, as well as intolerance to heat or cold. These problems can be particularly uncomfortable and affect the ability to perform daily activities.
Breathing problems and sleeping difficulties
Breathing and sleep rhythm disorders are also common in dysautonomia. Patients may experience episodes of rapid or shallow breathing and difficulty controlling breathing under stress or during exercise. In addition, dysautonomia can affect sleep patterns, resulting in insomnia, interrupted sleep or, in some cases, hypersomnia. These problems affect not only the quality of sleep, but also the general well-being and resilience of the body.
Each of these symptoms presents its own challenges, and their management requires a comprehensive and personalised approach, highlighting the importance of appropriate assessment and treatment to improve the quality of life of those suffering from dysautonomia. At this point, NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation of the autonomic nervous system is presented as an optimal option to treat this type of ailment. We explain how.
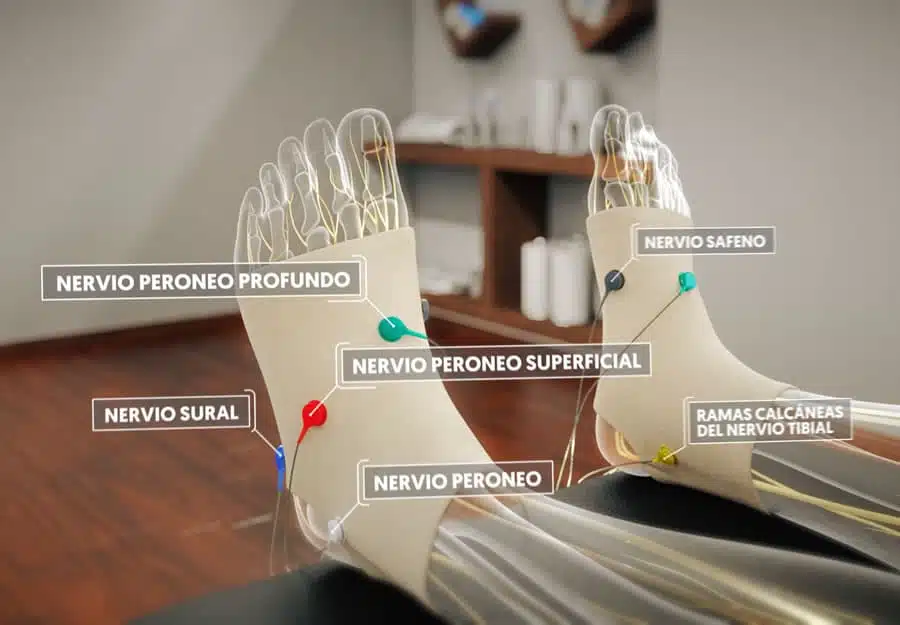
What is NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation and how does it work?
Treatments and management of dysautonomia
NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation
The advanced medical technology of NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation represents a promising advance in the treatment of dysautonomia. This type of therapy sends mild electrical impulses to the nervous system with the aim of ‘resetting’ and optimising its functioning. By specifically stimulating certain areas, autonomic regulation can be positively influenced, thus improving dysautonomia symptoms without the need for surgical interventions. The technology is non-invasive and painless for the patient, with short and medium-term results that are maintained over time.
Benefits of non-invasive neuromodulation
- The electrical impulses of NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation are used as a complementary treatment to mitigate pain, recovering mobility and muscle tone.
- It can also be used as a preventive technique to avoid injury or the appearance of pain in chronic illnesses.
- It is also applied in the field of sports to help improve the physical performance of athletes in their training sessions, notably recovering muscle fatigue and improving their quality of sleep.
- In the urogynaecological field, its use is beneficial for treating ailments such as overactive bladder syndrome, erectile dysfunction and/or other problems related to the pelvic floor.
Tips for caring for the autonomic nervous system
Protecting and strengthening the ANS is vital to prevent or manage dysautonomia. Here are some practical tips to keep your autonomic nervous system in perfect balance:
- Keep a regular schedule: Establishing routines for mealtimes, bedtimes and physical activity can help regulate the ANS.
- Moderate exercise: Activities such as walking, swimming or yoga exercises can improve autonomic function by stimulating the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system in a balanced way.
- Balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains and low in processed sugars and trans fats should be a must. In this way, you support the health of the ANS, improving your overall health.
- Relaxation techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing and mindfulness can reduce stress, lower your cortisol levels and promote a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- Avoid stimulants: Reducing or avoiding caffeine and nicotine intake can be beneficial, as these substances can disrupt the functioning of the ANS.
- Adequate hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for the optimal functioning of the nervous system and to prevent symptoms such as orthostatic hypotension, which we discussed above.
- Professional consultation: For recurrent or worrisome symptoms, it is essential to seek the guidance of a health professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and suggest specific treatments, including approaches such as non-invasive neuromodulation.
Holistic body care in today's age
We live in an age of unprecedented technological advances, where medical science has progressed by leaps and bounds, allowing us to better understand and treat conditions as complex as dysautonomia. Despite these advances, the prevalence of autonomic nervous system disorders reminds us of the importance of taking care of our body and mind with a holistic approach.
The fast pace of modern life often places stress on our autonomic nervous system, underscoring the need to adopt practices that promote balance and overall wellbeing. Non-Invasive Neuromodulation, NESA®, emerges as a valuable tool, complementing traditional health and wellness strategies. However, prevention remains key. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, attending to our physical and emotional needs, and seeking medical advice when necessary, are essential steps in protecting this vital system.
The future of autonomic nervous system care
In short, by taking care of our autonomic nervous system, we are not only preventing dysautonomia and other disorders, but we are also improving our quality of life in every way. It is time for each person to take an active role in taking care of their health, adapting the knowledge and technologies available to live a fuller and healthier life.
Before we finish, we would like to ask you a question, do you think it is important to take care of the autonomic nervous system? We'll read you in the comments.
For health professionals
If you are a health professional and your answer is yes, we invite you to learn more about our NESA® Non Invasive Neuromodulation medical technology, please contact us.
Para pacientes
Si eres paciente y tienes interés en conocer cómo funciona la neuromodulación no invasiva, encuentra tu clínica más cercana con nuestra tecnología médica avanzada.